Chapter Two: Introduction
Conceptual Problems
Problem One
Part a)
Flexible Model. Due to the large number of datapoints that the training set accuratelyrepresents the predictors domain and therefore overfitting is less of a concern and a flexible model midll be appropriate.
Part b)
Non-Flexible. For opposite reasons to 1a. A low number of samples means that the training data may be a good representation of the of the feature domain and therefore there is a high chance of overfitting. This is enhanced due to the large predictor space making the domain even less representative of possible values in the test set.
Part c)
Flexible. A highly non-linear relationship would mean that non-flexible models would have a large bias and therefore flexible models will be needed to capture the non-linearity.
Part d)
Unknown. In this case there is not much we can do as our models can only affect the reducible error or the model (In the model variance and bias) but, by definition, cannot affect the irreducible error. The most likely cause of this large variance in the error is missing a fundamental predictor in the data/model.
Problem Two
| Part | Type of problem | n | p | inference | predictive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a) | Regression | 500 | 3 | Y | N |
| b) | Classification | 20 | 13 | N | Y |
| c) | Regression | 52 | 4 | N | Y |
Problem Three
Part a)
The variance, bias, test error, trianing error and Bayes error are plotted below.
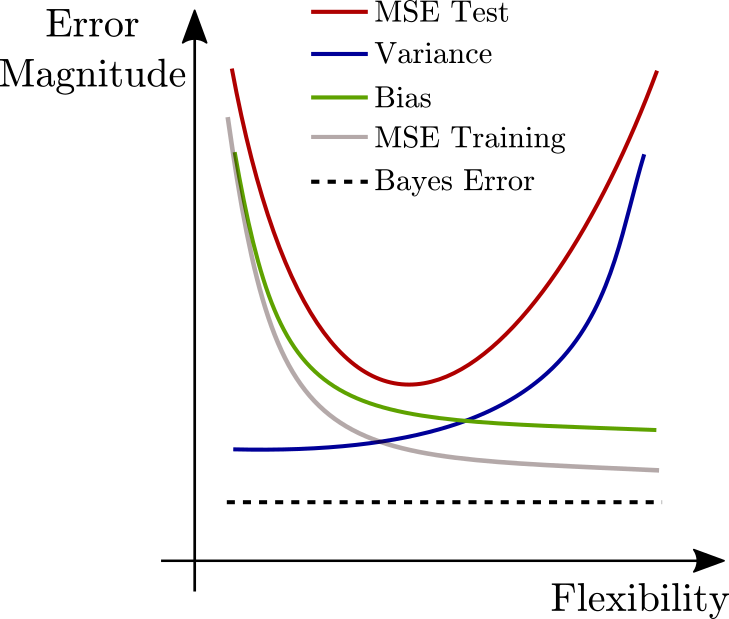
Part b)
Variance
In a highly inflexible model each datapoint will not have a large affect on the overall model. Therefore each model hypothesis from a different training set will not vary significantly (differ from some averge model hypothesis). The models will be accurate but not necessarily precise.
As the model becomes more flexible and tries to capture more of each training sets nature, each new training model will differ more than the inflexible case and therefore have a larger variance.
Bias
For inflexible models there is a large bias. Bias indicates how well the model in general differs from the true nature of a training set. For models with low flexibility the averge model hypothesis will differ largely from the true nature sample.
As the flexibility increases, the average model converges on the samples true nature and the bias decreases.
Training Error
As the flexibility of the model increases the bias of the model decreases and it can ore accurately fit the training data.
Test Error
The U-shape of the test error reflects the property of unfitting or overfitting the model on the training set. An inflexible model will underfit the training data, not capturing enough of the nature of the relationships and result in a high error.
Conversely, a very flexble model will overfit the training data, capturing too much of the noise of the training set and poorly fitting the out of sample test set.
Bayes Error Fundamental error of the model also known as irreducible error. This can arise from many things such as insufficient data collected for the problem. The training or test set errors cannot lie under these errors.
Problem Five
| Flexible | Non-Flexible |
|---|---|
| Poor for inference | Good for inference |
| High variance | Low variance |
| Low Bias | High Bias |
| High chance of overfitting | High chance of underfitting |
| Difficult to interpret results | Easier to interpret results |
Problem Six
Parametric approaches are those which model a system with a set of statistical parameters. For example linear regression is a parametric model where the graadients and intercept are the parameters. A nonparametric approach is one which does not use these distinct parameters, for example a decsion tree model. Each has their advantages, parametric models are typically more interpretable but less flexible than non-parametric models and therefore have a higher bias. These non parametric forms do not assume a functional form of the relationship between the target and the predictors unline the parametric models.
Problem Seven
Part a)
| Point | distance |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | $\sqrt{10}$ |
| 4 | $\sqrt{5}$ |
| 5 | $\sqrt{2}$ |
| 6 | $\sqrt{3}$ |
Part b)
For $K=1$ the nearest point is 5 and therefore it would be classified as 'Green'. For $K=3$ the nearest points are {'Red', 'Red', 'Green'} and therefore it will be classified as 'Red'.