Chapter Two: Introduction
Applied Problems
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import os
Problem Eight
Part a)
Using pandas we can load the data:
college_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'college.csv'))
Part b)
Index the dataframe so that college names are the index:
## Set the column index to the College name
college_df.rename(columns={college_df.columns[0] : "College"}, inplace=True)
college_df.set_index("College", inplace=True)
Part c)
i.
Numerical summary of the college data:
print(college_df.describe())
Apps Accept Enroll Top10perc Top25perc F.Undergrad P.Undergrad ... Personal PhD Terminal S.F.Ratio perc.alumni Expend Grad.Rate
count 777.000000 777.000000 777.000000 777.000000 777.000000 777.000000 777.000000 ... 777.000000 777.000000 777.000000 777.000000 777.000000 777.000000 777.00000
mean 3001.638353 2018.804376 779.972973 27.558559 55.796654 3699.907336 855.298584 ... 1340.642214 72.660232 79.702703 14.089704 22.743887 9660.171171 65.46332
std 3870.201484 2451.113971 929.176190 17.640364 19.804778 4850.420531 1522.431887 ... 677.071454 16.328155 14.722359 3.958349 12.391801 5221.768440 17.17771
min 81.000000 72.000000 35.000000 1.000000 9.000000 139.000000 1.000000 ... 250.000000 8.000000 24.000000 2.500000 0.000000 3186.000000 10.00000
25% 776.000000 604.000000 242.000000 15.000000 41.000000 992.000000 95.000000 ... 850.000000 62.000000 71.000000 11.500000 13.000000 6751.000000 53.00000
50% 1558.000000 1110.000000 434.000000 23.000000 54.000000 1707.000000 353.000000 ... 1200.000000 75.000000 82.000000 13.600000 21.000000 8377.000000 65.00000
75% 3624.000000 2424.000000 902.000000 35.000000 69.000000 4005.000000 967.000000 ... 1700.000000 85.000000 92.000000 16.500000 31.000000 10830.000000 78.00000
max 48094.000000 26330.000000 6392.000000 96.000000 100.000000 31643.000000 21836.000000 ... 6800.000000 103.000000 100.000000 39.800000 64.000000 56233.000000 118.00000
ii.
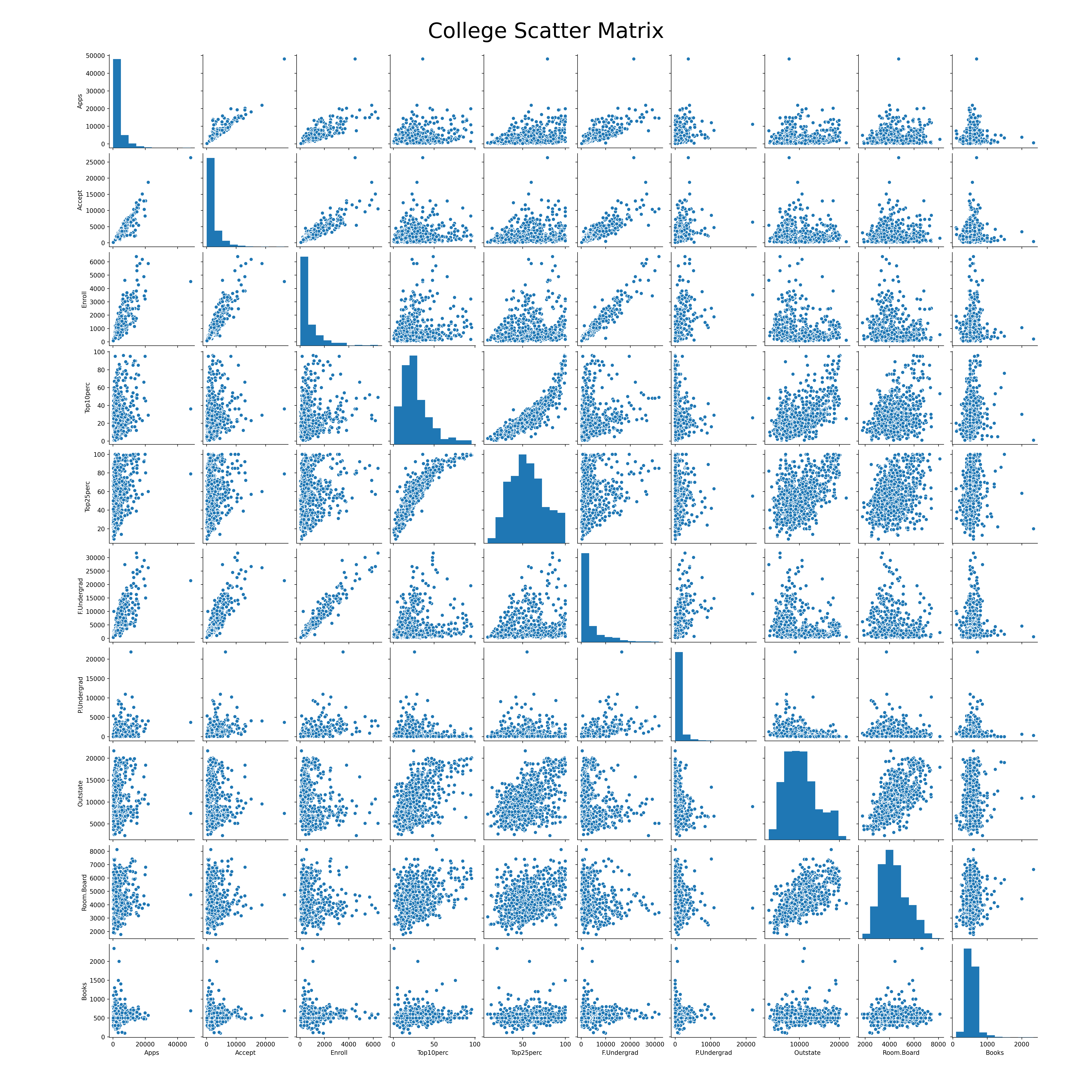
Plotting the scatter matrix of the first 11 columns using seaborn,
## Plot the scatter matrix of the first 11 numerical columns
ax1 = sns.pairplot(college_df[college_df.columns[0:11]])
plt.gcf().subplots_adjust(bottom=0.05, left=0.1, top=0.95, right=0.95)
ax1.fig.suptitle('College Scatter Matrix', fontsize=35)
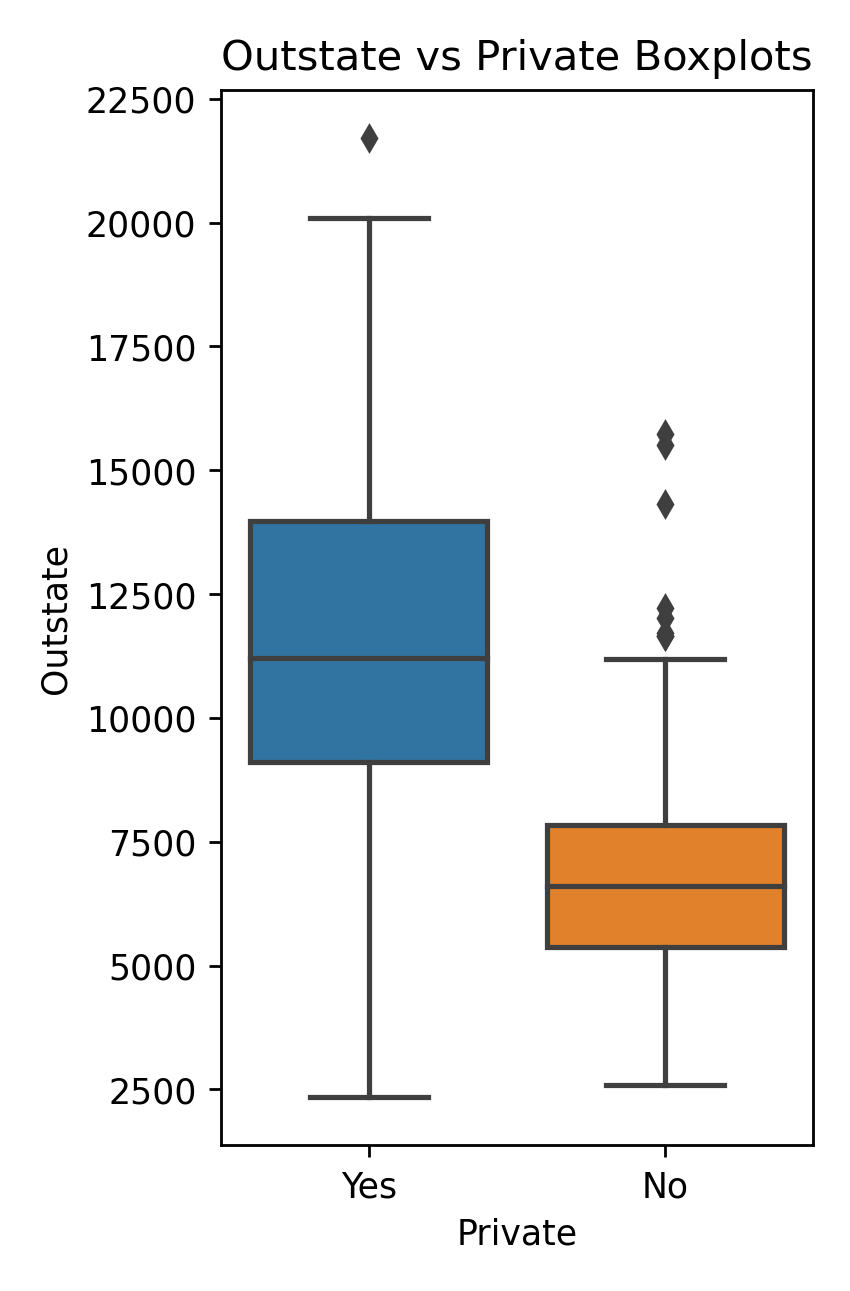
iii.
Produce the boxplots of the Outstate vs Private
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
sns.boxplot(ax=ax, x="Private", y="Outstate", data=college_df)
plt.title(r'Outstate vs Private Boxplots')
width = 3.403
height = 1.518*width
fig.set_size_inches(width, height)
fig.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig(os.path.join(IMAGE_DIR,'Outstate_Private_boxplot.png'), format='png', dpi=250)
plt.show()
plt.close()
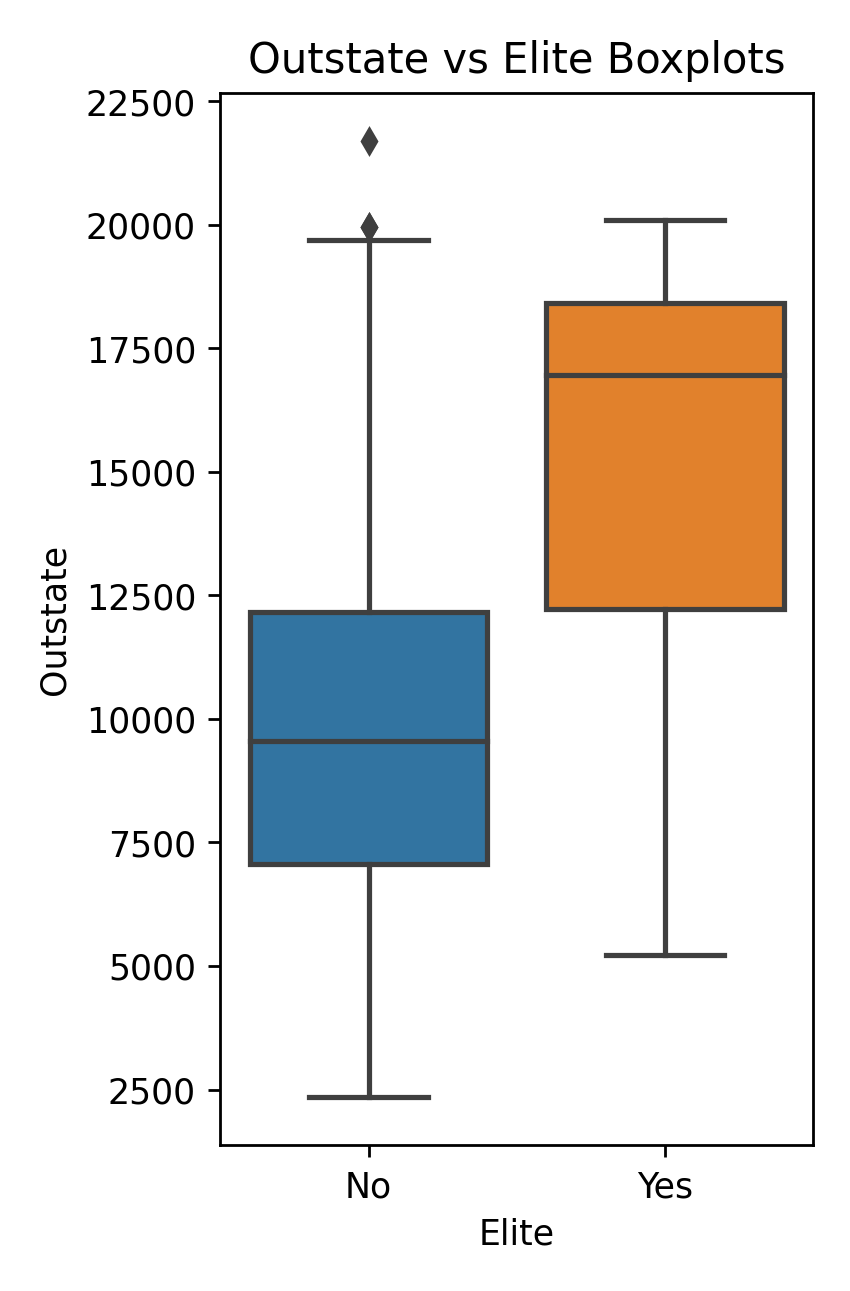
iv.
Create the new column with pandas:
college_df['Elite'] = pd.Series(len(college_df['Top10perc']), index=college_df.index)
college_df['Elite'] = 'No'
college_df.loc[college_df['Top10perc']>50,'Elite'] = 'Yes'
num_elite = college_df[college_df['Elite'] == 'Yes']['Elite'].count()
Plot the boxplot of Outstate vs Elite
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
sns.boxplot(ax=ax, x="Elite", y="Outstate", data=college_df)
plt.title(r'Outstate vs Elite Boxplots')
width = 3.403
height = 1.518*width
fig.set_size_inches(width, height)
fig.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig(os.path.join(IMAGE_DIR,'Outstate_Elite_boxplot.png'), format='png', dpi=250)
plt.show()
plt.close()
Problem Nine
Part a)
## Import auto.csv from DATA_DIR
auto_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'auto.csv'))
## Print out missing values
print(auto_df.isna().sum())
print(auto_df.describe())
### a) Print out qualitative and quantitative columns
numeric_types = ['int16', 'int32', 'int64', 'float16', 'float32', 'float64']
object_types = ['object']
quantitative = auto_df.select_dtypes(include=numeric_types).columns
qualitative = auto_df.select_dtypes(include=object_types).columns
# print("All features : " + str(auto_df.columns.format()))
print("Quantitative features: " + str(quantitative.format()))
print("Qualitative features: " + str(qualitative.format()))
Quantitative features: ['mpg', 'cylinders', 'displacement', 'weight', 'acceleration', 'year', 'origin']
Qualitative features: ['horsepower', 'name']
Here horsepower has been classified as qualitatife due to a single value only. This will need to be processed to properly classify the column.
Part b)
for feature in quantitative:
print(feature + ' range: ' + str(auto_df[feature].describe()['min']) + ' to ' + str(auto_df[feature].describe()['max']))
mpg range: 9.0 to 46.6
cylinders range: 3.0 to 8.0
displacement range: 68.0 to 455.0
weight range: 1613.0 to 5140.0
acceleration range: 8.0 to 24.8
year range: 70.0 to 82.0
origin range: 1.0 to 3.0
Part c)
for feature in quantitative:
print(feature + ' mean: ' + str(round(auto_df[feature].describe()['mean'], 2)) + ' , std. dev.: ' + str(round(auto_df[feature].describe()['std'], 2)))
mpg mean: 23.52 , std. dev.: 7.83
cylinders mean: 5.46 , std. dev.: 1.7
displacement mean: 193.53 , std. dev.: 104.38
weight mean: 2970.26 , std. dev.: 847.9
acceleration mean: 15.56 , std. dev.: 2.75
year mean: 75.99 , std. dev.: 3.69
origin mean: 1.57 , std. dev.: 0.8
Part d)
auto_dropped = auto_df.drop(auto_df.index[10:86])
# print(auto_dropped)
for feature in quantitative:
print(feature + ' range: ' + str(auto_dropped[feature].describe()['min']) + ' to ' + str(auto_dropped[feature].describe()['max']))
for feature in quantitative:
print(feature + ' mean: ' + str(round(auto_dropped[feature].describe()['mean'], 2)) + ' , std. dev.: ' + str(round(auto_dropped[feature].describe()['std'], 2)))
mpg range: 11.0 to 46.6
cylinders range: 3.0 to 8.0
displacement range: 68.0 to 455.0
weight range: 1649.0 to 4997.0
acceleration range: 8.5 to 24.8
year range: 70.0 to 82.0
origin range: 1.0 to 3.0
mpg mean: 24.44 , std. dev.: 7.9
cylinders mean: 5.37 , std. dev.: 1.65
displacement mean: 187.17 , std. dev.: 99.86
weight mean: 2933.18 , std. dev.: 809.64
acceleration mean: 15.71 , std. dev.: 2.71
year mean: 77.14 , std. dev.: 3.13
origin mean: 1.6 , std. dev.: 0.82
Problem Ten
Load in the dataset
## Load the boston dataset
boston_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'boston.csv'))
Part a)
Get a general breakdown of the data:
print('Numerical Breakdown of quant. variables: \n')
print(boston_df.describe())
print("Total number of columns: ", len(boston_df.columns))
print("Column Names:")
for col in boston_df.columns:
print(col)
Numerical Breakdown of quant. variables:
CRIM ZN INDUS CHAS NOX RM AGE DIS RAD TAX PTRATIO B LSTAT target
count 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000
mean 3.613524 11.363636 11.136779 0.069170 0.554695 6.284634 68.574901 3.795043 9.549407 408.237154 18.455534 356.674032 12.653063 22.532806
std 8.601545 23.322453 6.860353 0.253994 0.115878 0.702617 28.148861 2.105710 8.707259 168.537116 2.164946 91.294864 7.141062 9.197104
min 0.006320 0.000000 0.460000 0.000000 0.385000 3.561000 2.900000 1.129600 1.000000 187.000000 12.600000 0.320000 1.730000 5.000000
25% 0.082045 0.000000 5.190000 0.000000 0.449000 5.885500 45.025000 2.100175 4.000000 279.000000 17.400000 375.377500 6.950000 17.025000
50% 0.256510 0.000000 9.690000 0.000000 0.538000 6.208500 77.500000 3.207450 5.000000 330.000000 19.050000 391.440000 11.360000 21.200000
75% 3.677082 12.500000 18.100000 0.000000 0.624000 6.623500 94.075000 5.188425 24.000000 666.000000 20.200000 396.225000 16.955000 25.000000
max 88.976200 100.000000 27.740000 1.000000 0.871000 8.780000 100.000000 12.126500 24.000000 711.000000 22.000000 396.900000 37.970000 50.000000
Total number of columns: 14
Column Names:
CRIM
ZN
INDUS
CHAS
NOX
RM
AGE
DIS
RAD
TAX
PTRATIO
B
LSTAT
target
Part b)
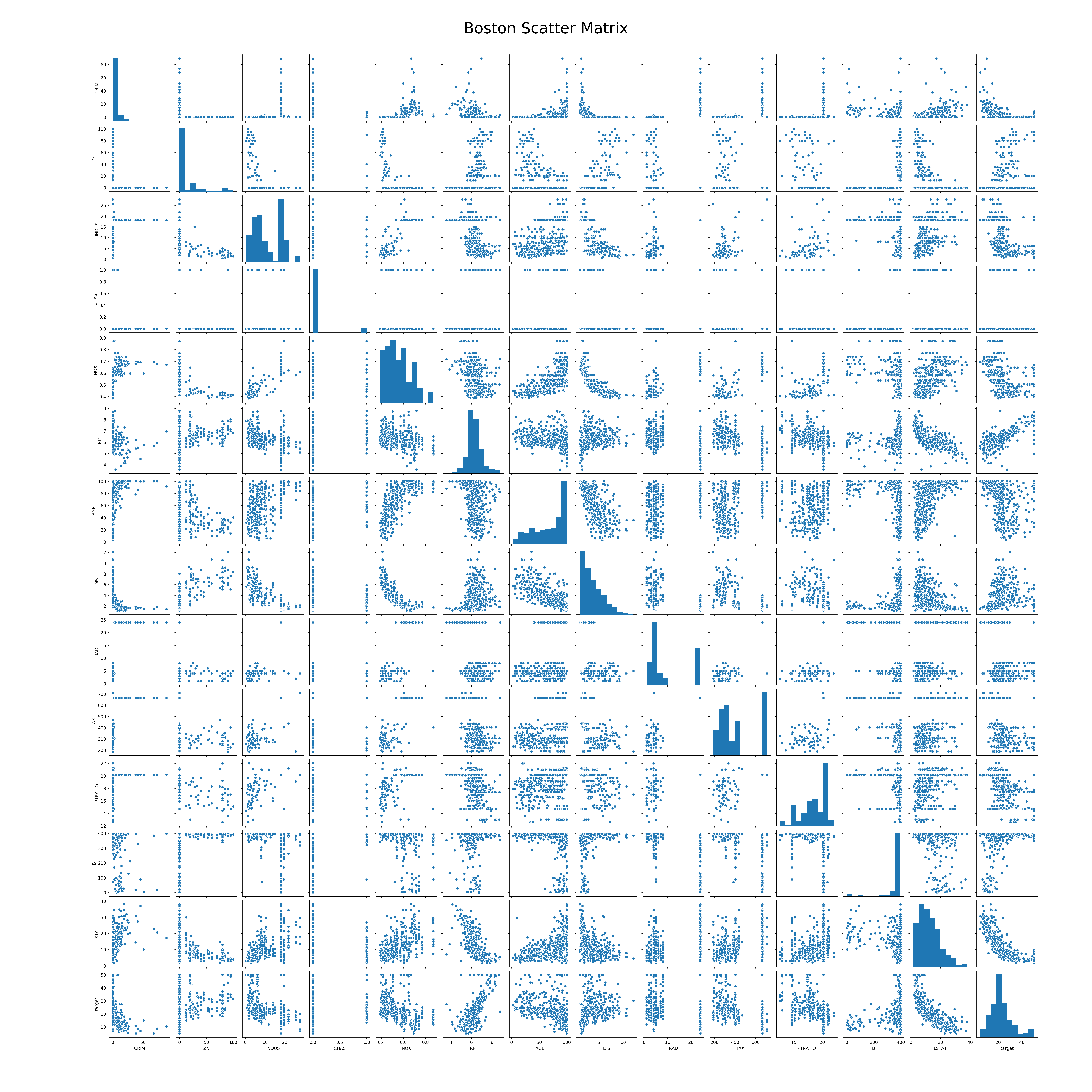
Generate the scatterplot matric for the dataset:
ax1 = sns.pairplot(boston_df)
plt.gcf().subplots_adjust(bottom=0.05, left=0.1, top=0.95, right=0.95)
ax1.fig.suptitle('Boston Scatter Matrix', fontsize=35)
plt.savefig(os.path.join(IMAGE_DIR,'boston_scatter_matrix.png'), format='png', dpi=250)
plt.show()